Backup and Restore with YubiHSM Backup Keys
This document describes methods for creating a secondary YubiHSM key that is a backup of your primary YubiHSM. Topics in this document:
Backup using Shell, Setup, or KSP
The YubiHSM 2 supports encrypted export and import of objects using a symmetric AES-CCM based scheme.
The examples below assume the default authentication key (0x0001). If you use some other authentication key make sure that it has the capability put-wrap-key and has the correct delegated capabilities, otherwise you will get a wrong permissions for operation error.
You can perform these operations using:
- YubiHSM Shell for backing up and restoring
- YubiHSM Setup for backing up and restoring
- YubiHSM Key Storage Provider for backing up and restoring certificate as well as private key.
Basic steps for all three cases:
- Create a wrap key, call it wrapkey.
- Import wrapkey into the primary YubiHSM2.
- Export other objects in the primary YubiHSM2 using wrapkey.
- Import wrapkey into the backup YubiHSM2.
- Import the objects exported in step 3 into the backup YubiHSM2.
Conditions required for a successful full backup: Any object that does not fulfill these conditions is not exported:
- wrapkey is accessible in all the domains the other objects are available in.
- wrapkey has delegated capabilities that include all the capabilities any other object has.
- wrapkey has the capabilities
export-wrappedandimport-wrapped. - All other objects have the capability
exportable-under-wrap.
Backup and Restore Using YubiHSM Shell
Backup
Start by generating an asymmetric key that we then make a backup of.
$ yubihsm-shell -a generate-asymmetric-key -A rsa2048 --capabilities exportable-under-wrap, sign-pkcs,decrypt-pkcs ... Generated Asymmetric key 0x6e77 ...
This generates an asymmetric key accessible in all domains.
Get a pseudo random number from the YubiHSM2 and store it in a file. This is the wrap key.
$ yubihsm-shell -a get-pseudo-random --count=32 --out=wrap.key
Important
The file
wrap.keyhere contains the Wrap Key loaded into your YubiHSM in clear text. It should therefore be considered sensitive.Import
wrap.keyinto the primary YubiHSM2.... yubihsm-shell -a put-wrap-key --capabilities export-wrapped,import-wrapped --delegated=sign-pkcs, decrypt-pkcs,exportable-under-wrap --in=wrap.key ... Stored Wrap key 0xd581
This imports a wrap key accessible in all domains.
Make an encrypted backup of the Asymmetric Key
0x6e77in the filekey_6e77.yhw.yubihsm-shell -a get-wrapped --wrap-id=0xd581 --object-id=0x6e77 -t asymmetric-key --out=key_6e77.yhw
Restore
This step assumes you have a fresh device where you want to restore the previously backed up key 0x6e77.
Import the wrap key into the backup YubiHSM2.
$ yubihsm-shell -a put-wrap-key -A aes256-ccm-wrap -c export-wrapped, import-wrapped --delegated=sign-pkcs,decrypt-pkcs,exportable-under-wrap --in=wrap.key -i 0xd581 ... Stored Wrap key 0xd581
Import the Asymmetric key
0x6e77into the backup YubiHEM2.yubihsm-shell -a put-wrapped --wrap-id=0xd581 --in=key_6e77.yhw ... Object imported as 0x6e77 of type asymmetric-key
Backup and Restore Using YubiHSM Setup
The YubiHSM 2 Setup Tool can be used to backup and restore all exportable objects simultaneously.
Backup
The step here assumes that a wrap key fulfilling all the conditions mentioned above already exists in the primary YubiHSM2. For the following command line examples, assume that such a key has ObjectID 0xd581.
$ yubihsm-setup dump
Enter the wrapping key ID to use for exporting objects: 0xd581
...
Successfully exported object Asymmetric with ID 0x6e77 to ./0x6e77.yhw
All done
Note
When creating a wrap key using yubihsm-setup with the subcommand ksp or ejbca, an option is presented to split the wrap key into shares to be held by different custodians. It would also be possible to set the minimum number of custodians required to reconstruct the wrap key.
Important
Split and reconstruction of the wrap key is done in the software (yubihsm-setup). The YubiHSM2 itself is not aware of such split or any shares.
Restore
Running the store command imports all \*.yhw files in the current directory. If some of those files are not encrypted and wrapped with a wrap key that exists in the backup YubiHSM2, they are not imported.
$ yubihsm-setup restore
Note
If the wrap key was split, the shares to reconstruct it need to be provided in this step.
Backup and Restore Using YubiHSM KSP (Windows Only)
YubiHSM Key Storage Provider (KSP) enables backing up and restoring the keys managed using this tool.
Note
Microsoft Active Directory Certificate Services (ADCS) does not set the NCRYPT_ALLOW_EXPORT_FLAG when generating a key, either through the setup UI or the Install-ADCSCertificationAuthority PowerShell module.
When creating an ADCS root CA key using the YubiHSM 2, the exportable-under-wrap Capability is added by default. Backup and restore functionality is therefore available using the following manual processes.
- Identify Your Private Key Container Name
- Backup the Target Certificate
- Backup the Target Private Key
- Restore the Target Private Key
- Restore the Target Certificate
Identify Your Private Key Container Name
- To view the currently installed certificates in the Local Machine “My” store, open an elevated command prompt/shell by using the
certutilcommand.
PS1> certutil -store My
- Find the target certificate in the list and then find its
Key Containerproperty. The Provider property should be the same asYubiHSM Key Storage Provider. - To identify the certificate, record the
Cert Hashproperty.
Backup the Target Certificate
Using any available means (certmgr.msc, PowerShell, certutil), export the target certificate, but without the private key in DER format.
Note
The YubiHSM does not provide a mechanism for returning the raw private key to Windows, so generating a PKCS#12 container is not currently possible.
For example, to export the certificate in .crt ``format to a file named ``<Cert Hash>.crt, use the command.
PS1> certutil -split -store My <Cert Hash>.
Backup the Target Private Key
Export the target private key with the label property equal to the Key Container property.
- Use an Authentication Key with the
export-wrappedcapability set. - Use the instructions for exporting a private key under wrap via
yubihsm-shell(see Backup and Restore Using YubiHSM Shell).
Restore the Target Private Key
Import the target private key file to your backup YubiHSM.
- Use an Authentication Key with the
import-wrappedcapability set. - Use the instructions for importing a private key under wrap via
yubihsm-shell(see Backup and Restore Using YubiHSM Shell).
The imported key object should have the same Label property as the original object.
Restore the Target Certificate
Before the certificate is imported to the local machine, it does not have an associated private key.
- Move the target certificate file generated as per Backup and Restore Using YubiHSM Shell to the target machine by importing the certificate to the LocalMachine “My” store. Use your preferred method.
- Re-associate the certificate to the private key by using the
-repairstorefunctionality ofcertutil. - Verify that the target private key is visible via the YubiHSM KSP: list all private keys (and their corresponding container names - which are equal to the
Labelproperty in the YubiHSM visible to the current Authentication Key).
PS1> certutil -key -csp "YubiHSM Key Storage Provider"
- Open an elevated prompt and execute the command:
PS1> certutil -repairstore MY <Cert Hash>
- To verify that the certificate has been associated with the YubiHSM Key Storage Provider and has the correct
Key Containerproperty value, repeat the steps under Identify Your Private Key Container Name.
Backup Examples
We strongly recommend you make a backup copy of all production objects residing on your primary device, particularly once the CA root key has been generated on the device. If there is an unforeseen hardware failure of the primary device, having a backup ensures that you can resume operations quickly. In addition, this provides a means to backup all objects contained on a device to reside in secure hardware offline.
The backup process results in two identical YubiHSM 2 devices with the same number of objects, keys, labels, etc.
Note
Specific recommendations for governance of your critical key material is out of scope for this guide. Ensure that you design and document these security procedures to fit the requirements of your organization. In many cases, they are subject to audits.
Backup and Restore the YubiHSM 2 Overview
The backup, see Backup using Shell, Setup, or KSP, of the primary YubiHSM 2 is a duplicate of all of the objects stored on the primary device. The objects are exported under wrap onto the secondary device. The objects are available using the same application authentication key used.
For instance, when following this example, the wrap key (created with ID 2 previously), the application authentication key (ID 3), the audit key (ID 4) (if created previously), and the CA root key is duplicated onto the secondary device. The factory-installed authentication key (ID 1) on the secondary device is destroyed. You need assistance from the wrap key custodians to provide their respective wrap key shares, if applicable.
In the example we used, 2 out of the 3 shares must be available. When you create a backup, you create a duplicate of the objects on your primary YubiHSM 2 onto a secondary device.
The backup and restore procedure consists of the steps listed below the following diagram. These steps are described in detail in the section, Restore Keys on the Secondary YubiHSM 2.
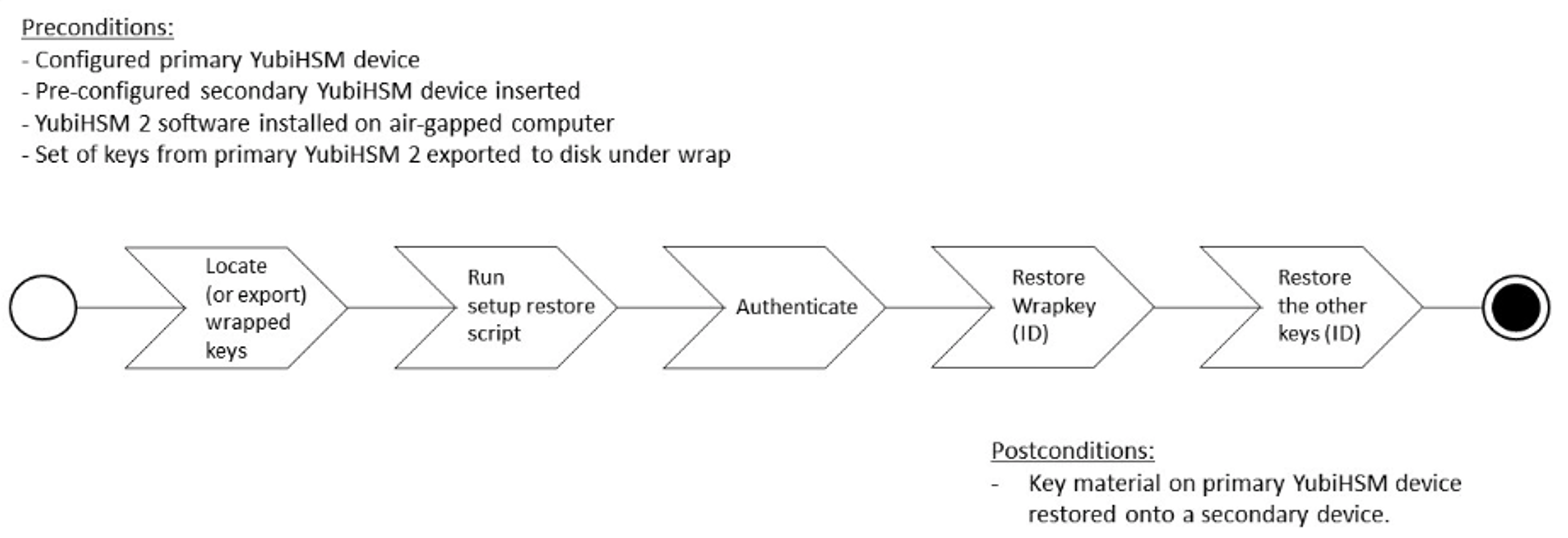
Figure: Backup and recovery on YubiHSM 2 Primary keys
- Locate the wrapped key material that was previously exported by the steps in YubiHSM 2 Key Storage Provider (KSP).
- Set up communication between the YubiHSM 2 tools and the secondary (backup) YubiHSM 2 device.
- Start the configuration process and authenticate to the secondary YubiHSM 2 device.
- Identify the CA root key ID.
- Export the CA root key.
- Verify the key material under wrap.
- Restore the key material onto a secondary (backup) YubiHSM 2 device.
- Verify the objects on the secondary device are correct.
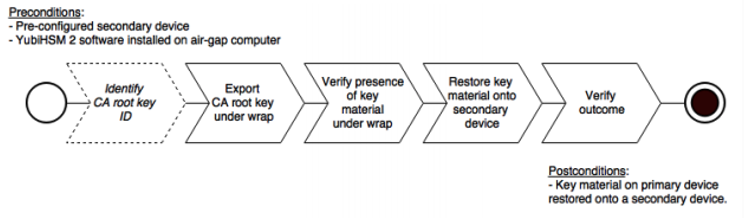
Figure: Recovery to YubiHSM 2 Secondary keys
Tip
For test purposes you can set the yubihsm-setup -d flag to keep the default authentication-key with the administrative privileges. This allows you to delete keys on the YubiHSM 2 for test purposes only. For production purposes however, the yubihsm-setup command must be executed without the -d flag to ensure that the factory preset authentication key is properly deleted on the YubiHSM 2.
Symmetric Backup of the Primary YubiHSM 2
The backup of the primary YubiHSM 2 is a duplicate of all of the objects stored on the primary device, to be exported under wrap and that are available using the application authentication key used.
The example described here is appropriate for testing and for smaller installations, such as those whose setup involved the YubiHSM Setup program. This example is not appropriate for moving the YubiHSM 2 device from one server to another.
This example gives instructions for duplicating the following on the secondary device:
- Wrapkey (previously created with ID
2), - Application authentication key (ID
3), - Audit key (ID
4) (if created previously)
The listed objects are exported under wrap.
The factory-installed authentication key (ID 1) on the secondary YubiHSM 2 device will be destroyed, just as it was on the primary YubiHSM 2 device.
If you use actual wrap key custodians (instead of just doing a proof of concept), you need the custodians to provide their respective wrap key shares. In the example we used in this guide, 2 out of the 3 custodians/shares must be available.
To guarantee integrity, perform these operations in an air-gapped environment.
Restore Keys on the Secondary YubiHSM 2
Since the CA root key was created on the device when setting up the CA, it currently only exists on the device. To back it up using the YubiHSM Setup program, it must first be exported from the device using the wrap key that also sits on the device alongside the application authentication key and the audit key. To export the CA root key under wrap using the wrap key on the device:
In your command line application, run YubiHSM Shell program. To do this, if you haven’t already:
Launch your command line application and navigate to the directory containing the YubiHSM Shell program.
Then run the following command and press Enter.
$ yubihsm-shell
To connect to the YubiHSM, at the
yubihsmprompt, typeconnectand press Enter. A message verifying that you have a successful connection is displayed.To open a session with the YubiHSM 2, type
session open 3and press Enter.Type in the
passwordfor the application authentication key.You will receive a confirmation message that the session has been set up successfully.
If you already know the object ID of the root CA, you can skip this step. If you need to identify the root CA, you can list the objects available.
- To list the objects, type
list objects 0(where0is the session number) and press Enter. - You receive a list of the objects on the device that the application authentication key with ID
3has access to, which includes the CA root key. Identify its ID.
- To list the objects, type
To export the CA root key under wrap from the primary device to the local file system, in the YubiHSM Shell program, run
yubihsm> get wrapped 0 2 seed=0 asymmetric-key {rootkeyID} rootkey.yhw
Where
seed=0does not export a privacy key seed. See EXPORT WRAPPED Command.Verify that all the keys, that were previously exported from the primary YubiHSM 2 under wrap, reside in the same directory as the YubiHSM Setup program and that you have read access to that directory.
If the necessary keys are not yet all available on disk, export the keys under wrap. Run the following command:
yubihsm-setup dumpThe YubiHSM Setup tool looks for files with the
.yhwfile extension in the current working directory and attempts to read and import them into the YubiHSM 2 device. The wrap key itself is imported when the wrap key shares are provided to the tool. For example, the following files may be present:0x0003-AuthenticationKey.yhw(Application authentication key under wrap)0x0004-AuthenticationKey.yhw(Audit key under wrap)rootkey.yhw(CA root key under wrap)x427a-Opaque.yhw(Certificate under wrap - not referenced by this guide in the configuration of the primary HSM 2)x427a-AsymmetricKey.yhw(Private asymmetric key under wrap - not referenced by this guide in the configuration of the primary HSM 2)
If the initial authentication key (by default available as ID
0x0001) has been deleted, the new authentication application key is identified with the flagyubihsm-setup --authkey. For example:$ yubihsm-setup --authkey 0x0003 dump
To begin the process of restoring the data onto the secondary YubiHSM 2, if the primary YubiHSM 2 device is inserted into your computer, remove it and insert the secondary device.
Important
Restoring a device must be performed in an air-gapped environment in order to guarantee integrity.
In your command line application (where
$is the prompt), run YubiHSM Setup with the argumentrestore.Change the directory containing the
*.yhwfiles,Run
yubihsm-setupwith therestoreargument:$ yubihsm-setup restore
To start the YubiHSM Setup process. Type the default authentication key password:
passwordand press Enter.
A confirmation message confirms that the default authentication key was used and that you successfully have authenticated to the YubiHSM 2 device:
Using authentication key 0x0001
- When prompted, type the minimum number of wrap key shares required by the privacy threshold and press Enter.
The require number of wrap key shares were defined when you set up the primary YubiHSM 2 device. In this guide, we have specified that 2 shares are required to regenerate the key. These must be present in order to proceed.
- When prompted for share number
1: Have the wrap key custodian holding the first share input this information and press Enter. A message confirms that the share is received:
Received share 2-1WWmTQj5PHGJQ4H9Y2ouURm8m75QkDOeYzFzOX1VyMpAOeF3YKYZyAVdM0WY4GErclVuAC
- Continue to have each wrap key custodian enter the share information for each of the wrap key shares required to regenerate the wrap key. When the sufficient number of wrap key shares have been entered by the wrap key custodians, a final message is displayed indicating that the wrap key from the primary YubiHSM 2 is now on the secondary YubiHSM 2 as well:
Stored wrap key with ID 0x0002 on the deviceNote
The ID of the wrap key on the secondary device is the same as the ID of the wrap key on the primary device.
- Review the output to verify Certificate Authority (CA) root key was also generated and exported along with a private asymmetric key, both under wrap.
After the wrap key has been stored on the secondary YubiHSM 2 device, the YubiHSM Setup program reads the files containing the application authentication key, the CA root key, and, if applicable, the audit key that were saved to file under wrap during the configuration of the primary device.
The output below shows that in this case, the Certificate Authority (CA) root key was also generated and exported along with a private asymmetric key, both under wrap.
reading ./0x0004.yhw Successfully imported object Authkey, with ID 0x0004 reading ./0x0003.yhw Successfully imported object Authkey, with ID 0x0003 reading ./0x427a-AsymmetricKey.yhw Successfully imported object Asymmetric, with ID 0x427a reading ./0x427a-Opaque.yhw Successfully imported object Opaque, with ID 0x427a reading ./rootkey.yhw Successfully imported object Asymmetric, with ID {rootkeyID}
- Review the output to note if there are files containing wrapped objects with the
.yhwfile extension in this directory that were exported with a wrap key other than the one reconstituted by the shares here. The Setup tool attempts to read those too, but fails gracefully. The Setup tool only restores the files it can decrypt. - Wait for the restore process to finish and the setup tool informs you that the default, factory-installed authentication key has been deleted.
Previous authentication key 0x0001 deleted All doneThe YubiHSM Setup application exits.
Verify the Duplicated YubiHSM 2
With the steps in the previous sections completed, you now have a secondary (duplicate) of the YubiHSM 2 device configured with the three key objects you created on the primary YubiHSM 2 device earlier.
Confirm that the key objects are identical on both the secondary (configured in previous section) and the primary device (configured earlier).
At your command prompt, run the YubiHSM Shell program. To do this, if you haven’t already:
Launch your command line application and navigate to the directory containing the YubiHSM Shell program.
Then run the following command and press Enter.
$ yubihsm-shell
Connect to the YubiHSM 2, at the
yubihsmprompt, typeconnectand press Enter. A message confirms that you have a successful connection.Open a session with the YubiHSM 2, type
session open 3and press Enter.where -
3is the ID for your application authentication key.Type the password for the application authentication key. A message confirms that the session has been set up successfully.
List the objects, type
list objects 0and press Enter.where -
0is session number that was given to you in step 4. Replace0with your session number, if it is different.Review the output and verify that the secondary device now contains all of the key material that you intended to restore.
Depending on the order in which the keys under wrap were imported, the order of the enumerated keys on the secondary device may be different than on the primary device when using the list command. This has no practical implication and the object IDs are identical between the devices.
After you verify that the secondary device contains all of the key material that you intended to restore, remove the keys under wrap currently on file in the current working directory for the YubiHSM Setup program. The computer’s hard drive can be erased.